This example is for Wiring version 1.0 build 0100+. If you have a previous version, use the examples included with your software. If you see any errors or have comments, please let us know.
tmp102 temperature sensor by BARRAGAN (http://barraganstudio.com)
Demonstrates use of the Wire library reading data from the tmp102 temperature sensor On Wiring v1 boards the SCL and SDA pins are: 0 and 1 On Wiring S board the SCL and SDA pins are: 8 and 9
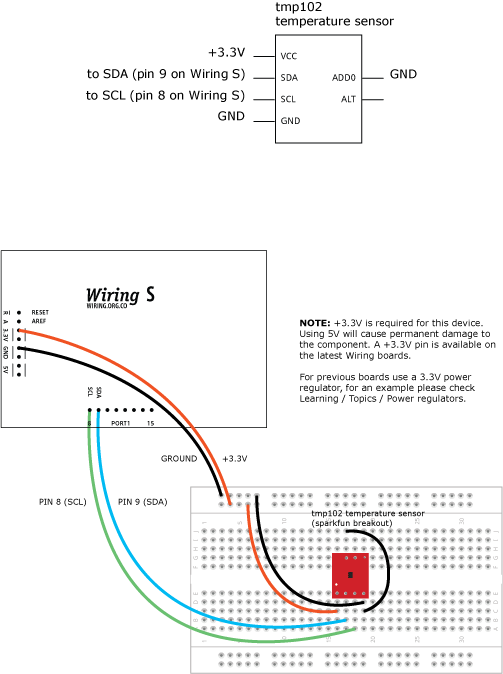
Demonstrates use of the Wire library reading data from the tmp102 temperature sensor On Wiring v1 boards the SCL and SDA pins are: 0 and 1 On Wiring S board the SCL and SDA pins are: 8 and 9

#include <Wire.h> // From the datasheet the BMP module address LSB distinguishes // between read (1) and write (0) operations, corresponding to // address 0x91 (read) and 0x90 (write). // shift the address 1 bit right (0x91 or 0x90), the Wire library only needs the 7 // most significant bits for the address 0x91 >> 1 = 0x48 // 0x90 >> 1 = 0x48 (72) int sensorAddress = 0x91 >> 1; // From datasheet sensor address is 0x91 // shift the address 1 bit right, the Wire library only needs the 7 // most significant bits for the address byte msb; byte lsb; int temperature; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // start serial communication at 9600bps Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master) } void loop() { // step 1: request reading from sensor Wire.requestFrom(sensorAddress,2); if (2 <= Wire.available()) // if two bytes were received { msb = Wire.read(); // receive high byte (full degrees) lsb = Wire.read(); // receive low byte (fraction degrees) temperature = ((msb) << 4); // MSB temperature |= (lsb >> 4); // LSB Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.println(temperature*0.0625); } delay(500); // wait for half a second }