This example is for Wiring version 1.0 build 0100+. If you have a previous version, use the examples included with your software. If you see any errors or have comments, please let us know.
I2C BOSCH BMP085 temperature and barometric pressure sensor based on code by Jean-Claude Wippler and Interactive Matter
Demonstrates use of the Wire library reading data from the BOSCH BMP085 temperature and barometric pressure sensor On Wiring v1 boards the SCL and SDA pins are: 0 and 1 On Wiring S board the SCL and SDA pins are: 8 and 9
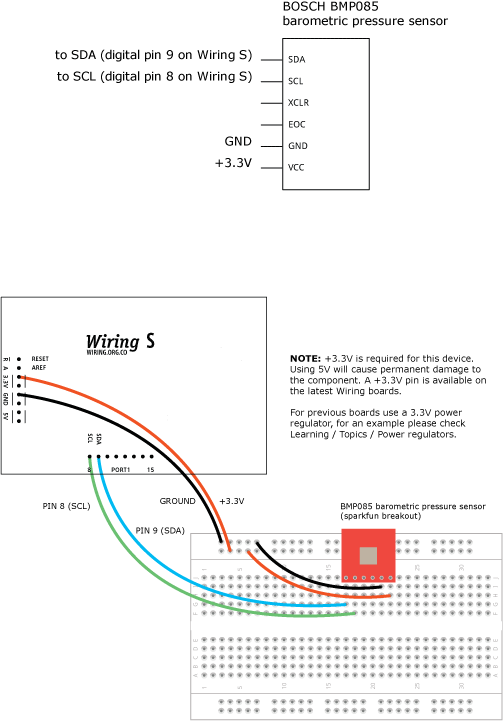
Demonstrates use of the Wire library reading data from the BOSCH BMP085 temperature and barometric pressure sensor On Wiring v1 boards the SCL and SDA pins are: 0 and 1 On Wiring S board the SCL and SDA pins are: 8 and 9

#include <Wire.h> // From the datasheet the BMP module address LSB distinguishes // between read (1) and write (0) operations, corresponding to // address 0xEF (read) and 0xEE (write). // shift the address 1 bit right (0xEF or 0xEE), the Wire library only needs the 7 // most significant bits for the address 0xEF >> 1 = 0x77 // 0xEE >> 1 = 0x77 int I2C_ADDRESS = 0x77; // sensor address // oversampling setting // 0 = ultra low power // 1 = standard // 2 = high // 3 = ultra high resolution const unsigned char oversampling_setting = 3; //oversampling for measurement const unsigned char pressure_conversiontime[4] = { 5, 8, 14, 26 }; // delays for oversampling settings 0, 1, 2 and 3 // sensor registers from the BOSCH BMP085 datasheet int ac1; int ac2; int ac3; unsigned int ac4; unsigned int ac5; unsigned int ac6; int b1; int b2; int mb; int mc; int md; // variables to keep the values int temperature = 0; long pressure = 0; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); Wire.begin(); getCalibrationData(); } void loop() { readSensor(); Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(temperature,DEC); Serial.print(" Pressure: "); Serial.println(pressure,DEC); delay(100); } // Below there are the utility functions to get data from the sensor. // read temperature and pressure from sensor void readSensor() { int ut= readUT(); long up = readUP(); long x1, x2, x3, b3, b5, b6, p; unsigned long b4, b7; //calculate true temperature x1 = ((long)ut - ac6) * ac5 >> 15; x2 = ((long) mc << 11) / (x1 + md); b5 = x1 + x2; temperature = (b5 + 8) >> 4; //calculate true pressure b6 = b5 - 4000; x1 = (b2 * (b6 * b6 >> 12)) >> 11; x2 = ac2 * b6 >> 11; x3 = x1 + x2; b3 = (((int32_t) ac1 * 4 + x3)<<oversampling_setting + 2) >> 2; x1 = ac3 * b6 >> 13; x2 = (b1 * (b6 * b6 >> 12)) >> 16; x3 = ((x1 + x2) + 2) >> 2; b4 = (ac4 * (uint32_t) (x3 + 32768)) >> 15; b7 = ((uint32_t) up - b3) * (50000 >> oversampling_setting); p = b7 < 0x80000000 ? (b7 * 2) / b4 : (b7 / b4) * 2; x1 = (p >> 8) * (p >> 8); x1 = (x1 * 3038) >> 16; x2 = (-7357 * p) >> 16; pressure = p + ((x1 + x2 + 3791) >> 4); } // read uncompensated temperature value unsigned int readUT() { writeRegister(0xf4,0x2e); delay(5); // the datasheet suggests 4.5 ms return readIntRegister(0xf6); } // read uncompensated pressure value long readUP() { writeRegister(0xf4,0x34+(oversampling_setting<<6)); delay(pressure_conversiontime[oversampling_setting]); unsigned char msb, lsb, xlsb; Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_ADDRESS); Wire.write(0xf6); // register to read Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(I2C_ADDRESS, 3); // request three bytes while(!Wire.available()); // wait until data available msb = Wire.read(); while(!Wire.available()); // wait until data available lsb |= Wire.read(); while(!Wire.available()); // wait until data available xlsb |= Wire.read(); return (((long)msb<<16) | ((long)lsb<<8) | ((long)xlsb)) >>(8-oversampling_setting); } void getCalibrationData() { Serial.println("Reading Calibration Data"); ac1 = readIntRegister(0xAA); Serial.print("AC1: "); Serial.println(ac1,DEC); ac2 = readIntRegister(0xAC); Serial.print("AC2: "); Serial.println(ac2,DEC); ac3 = readIntRegister(0xAE); Serial.print("AC3: "); Serial.println(ac3,DEC); ac4 = readIntRegister(0xB0); Serial.print("AC4: "); Serial.println(ac4,DEC); ac5 = readIntRegister(0xB2); Serial.print("AC5: "); Serial.println(ac5,DEC); ac6 = readIntRegister(0xB4); Serial.print("AC6: "); Serial.println(ac6,DEC); b1 = readIntRegister(0xB6); Serial.print("B1: "); Serial.println(b1,DEC); b2 = readIntRegister(0xB8); Serial.print("B2: "); Serial.println(b1,DEC); mb = readIntRegister(0xBA); Serial.print("MB: "); Serial.println(mb,DEC); mc = readIntRegister(0xBC); Serial.print("MC: "); Serial.println(mc,DEC); md = readIntRegister(0xBE); Serial.print("MD: "); Serial.println(md,DEC); } void writeRegister(unsigned char r, unsigned char v) { Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_ADDRESS); Wire.write(r); Wire.write(v); Wire.endTransmission(); } // read a 16 bit register int readIntRegister(unsigned char r) { unsigned char msb, lsb; Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_ADDRESS); Wire.write(r); // register to read Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(I2C_ADDRESS, 2); // request two bytes while(!Wire.available()); // wait until data available msb = Wire.read(); while(!Wire.available()); // wait until data available lsb = Wire.read(); return (((int)msb<<8) | ((int)lsb)); } // read an 8 bit register /* unsigned char readRegister(unsigned char r) { unsigned char v; Wire.beginTransmission(I2C_ADDRESS); Wire.send(r); // register to read Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(I2C_ADDRESS, 1); // request a byte while(!Wire.available()); // wait until data available v = Wire.receive(); return v; } */